In the vast realm of the internet, a domain name serves as your online address, your digital identity. But have you ever wondered what separates the components of a domain name? At Timely Domains, a prominent domain name investment company, we are here to unravel this mystery and shed light on the intricacies of this vital online asset.
With years of experience and expertise in the domain industry, our team is dedicated to helping businesses, entrepreneurs, and individuals secure domain names that elevate their online presence. From brandable domains that resonate with target audiences to exact match domains that boost search visibility, we carefully curate a portfolio of premium domain names. Our meticulous approach extends to expired domains as well, where we identify hidden gems with existing backlinks and domain authority.
Trust, transparency, and expertise are the cornerstones of our domain acquisition strategy. We not only offer a vast selection of premium domain names but also ensure fair and competitive pricing, along with personalized support throughout the buying and selling process. Timely Domains has an unmatched industry reputation, making us your trusted partner in acquiring and selling exceptional domain names. Get ready to take your online presence to new heights with Timely Domains – where expertise meets passion.
Components of a Domain Name
A domain name is a unique identifier that represents a website on the internet. It consists of several components that work together to create a memorable and functional online address. Understanding the various components of a domain name is essential for anyone looking to establish a strong online presence. In this article, we will explore the different components of a domain name in detail, including the top-level domain (TLD), second-level domain (SLD), subdomain, domain name extension, domain name registrar, domain name system (DNS), Whois information, domain name servers (DNS), host records, and domain name resolution.
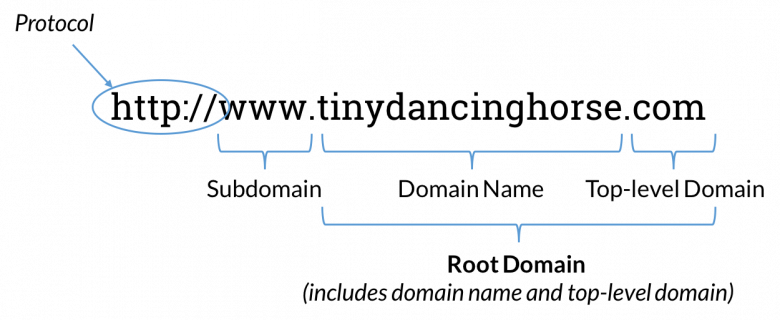
Top-Level Domain (TLD)
The top-level domain (TLD) is the highest level in the hierarchical domain name system. It is the part of the domain name that appears to the right of the dot, such as “.com,” “.org,” or “.net.” The TLD provides information about the purpose or nature of the website. For example, “.com” is commonly used for commercial websites, “.org” for non-profit organizations, and “.net” for network-related websites. There are also country code TLDs (ccTLDs) that are specific to individual countries, such as “.uk” for the United Kingdom or “.au” for Australia.

Second-Level Domain (SLD)
The second-level domain (SLD) is the part of the domain name that appears to the left of the dot and directly to the right of the TLD. It is the unique name chosen by the website owner and represents the main name of the website. For example, in the domain name “example.com,” the SLD is “example.” The SLD allows website owners to create a name that is memorable and relevant to their brand or business. It is an important component of a domain name as it helps in creating a distinctive online identity.
Subdomain
A subdomain is a part of a larger domain and is located to the left of the main domain name. It is separated from the main domain by a dot and is used to organize different sections or functions of a website. For example, in the domain name “blog.example.com,” the subdomain is “blog.” Subdomains allow website owners to create separate sections for blogs, forums, e-commerce, or any other specific content. They provide flexibility and help in organizing the various components of a website effectively.

Domain Name Extension
The domain name extension is the part of the domain name that follows the last dot. It provides additional information about the purpose or location of the website. Common domain name extensions include “.com,” “.org,” “.net,” and “.edu.” However, there are numerous other domain name extensions available that cater to specific industries or interests. For example, “.tech” is often used for technology-related websites, “.store” for e-commerce websites, and “.gov” for government websites.
Domain Name Registrar
A domain name registrar is a company or organization that manages the reservation and registration of domain names. They act as intermediaries between domain name owners and the domain name system (DNS). Domain name registrars allow individuals and businesses to search for and purchase available domain names. They also provide services such as domain name renewal, transfer, and DNS management. Popular domain name registrars include GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains.

Domain Name System (DNS)
The domain name system (DNS) is a decentralized system that translates domain names into IP addresses. Every website on the internet has a unique IP address, which is a series of numbers that identifies the location of the website’s server. The DNS acts as a directory that matches domain names to their corresponding IP addresses, allowing users to access websites by simply typing in the domain name. It plays a crucial role in facilitating the smooth and efficient functioning of the internet.
Whois Information
Whois information is a publicly accessible database that contains information about the registered owner of a domain name. This information includes the name of the domain owner, their contact details, the domain’s registration and expiration dates, and the domain’s nameservers. Whois information is essential for individuals and businesses looking to acquire or verify the ownership of a domain name. However, due to privacy concerns, some domain owners choose to protect their information by using privacy services offered by domain registrars.

Domain Name Servers (DNS)
Domain name servers (DNS) are specialized servers that store and distribute DNS records. They are responsible for translating domain names into corresponding IP addresses. There are different types of DNS servers, including authoritative DNS servers, recursive DNS servers, and caching DNS servers. These servers work together to ensure the accurate and efficient resolution of domain names to their respective IP addresses.
Host Records
Host records, also known as DNS records, are specific entries within the DNS that provide information about a domain or subdomain. These records include the IP address of the website’s server, mail server information, and other data required for the proper functioning of the website. Host records are essential for connecting domain names to their corresponding servers and enabling the correct routing of internet traffic.

Domain Name Resolution
Domain name resolution refers to the process of translating a domain name into its corresponding IP address. When a user enters a domain name in their web browser, their computer sends a request to a DNS server, asking for the IP address associated with that domain name. The DNS server then looks up the IP address in its database and returns it to the user’s computer, allowing the website to be accessed. Domain name resolution is a crucial part of browsing the internet and relies on the efficient functioning of the DNS.
Understanding the components of a domain name is essential for anyone looking to establish an online presence. By familiarizing yourself with the different components of a domain name, you can make informed decisions when registering, managing, or updating your domain. Whether it’s choosing the right TLD, SLD, or domain name extension, or understanding the role of DNS and domain name servers, each component plays a vital role in creating a successful and functional website.